Blog

We are excited to introduce version 3.40 of EasyMedStat, bringing two major improvements to streamline electronic patient-reported outcomes (ePRO) and enhance the patient experience. 🔄 Resume a Questionnaire from Where You Left Off Long questionnaires can be challenging to complete in one sitting. Now, if a patient stops answering a questionnaire, they can resume right from the last completed question . ✅ Saves time : No need to start over from the beginning. ✅ Ensures privacy : Previous answers are not displayed if someone else resumes the questionnaire. ✅ Improved tracking : A completed questionnaire is marked as "Completed", while an unfinished one remains "Partially completed". 🛠️ Smarter Handling of Empty Questionnaires Questionnaires sent to patients are now more intelligent: ✅ No more unnecessary intros and outros for empty sections. ✅ A questionnaire without any questions will not be sent , avoiding irrelevant emails. ✅ Real-time verification before sending ensures the questionnaire contains relevant data. ✅ Full transparency : If a questionnaire is canceled because it’s empty, its status is marked as "CANCELED", with an explanation. 🚀 Towards a More Seamless and Efficient Experience With this update, we take another step toward a more intuitive and automated ePRO management system. Less wasted time, more relevant data, and a better experience for everyone!
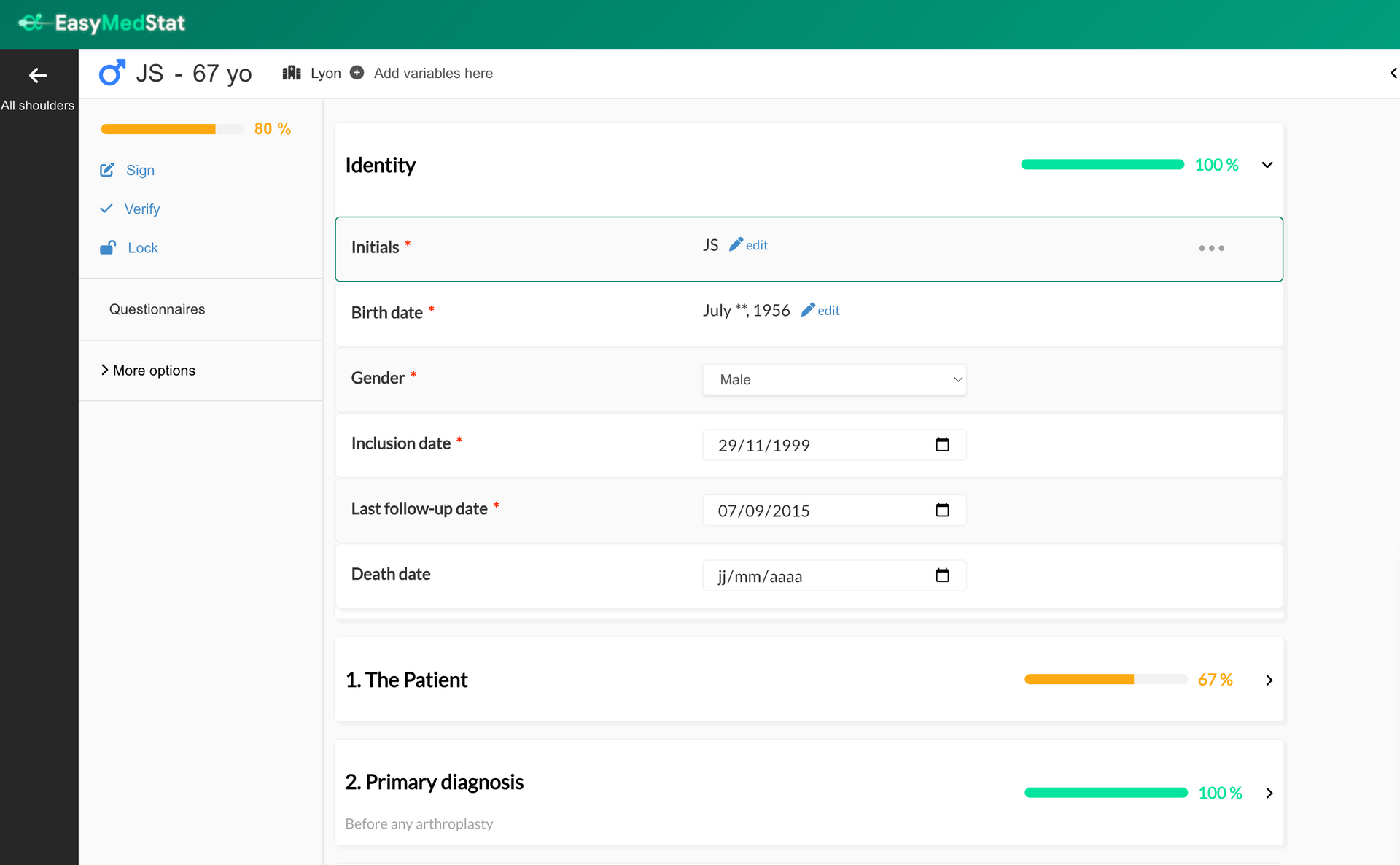
What’s new? Previously, you could only Sign, Verify, or Lock (SVL) an entire patient form at once. Now, you have more flexibility ! You can: ✅ Sign, verify, or lock individual categories (e.g., a specific visit) ✅ Sign, verify, or lock individual variables (e.g., a single data point) This means monitors and researchers no longer have to wait until the entire patient form is complete to start validating data. You can now review and confirm data as it becomes available ! Why is this useful? 🔹 Faster and more precise data validation – Approve data progressively instead of waiting for the full patient form. 🔹 Better tracking and accountability – Each signed, verified, or locked variable/category is timestamped and logged. 🔹 Stronger data integrity – Lock critical data points or visits to prevent unintended changes. How does it work? 1️⃣ Enable SVL per Category or Variable Go to Series Settings > Monitoring Activate "Allow sign, verify, and lock for each category" or "Allow sign, verify, and lock for each variable" These settings are OFF by default 2️⃣ New Icons for Each Category & Variable When enabled, you’ll see three new icons (Sign ✅, Verify ✔️, Lock 🔒) on each category and variable. Click an icon to sign, verify, or lock the corresponding data. 3️⃣ Security & Audit Trail A confirmation popup will appear when signing or verifying (not when locking). You must enter your password to confirm. All actions are logged in the audit trail for full traceability. 4️⃣ Permissions & Visibility Only users with Sign, Verify, or Lock permissions can perform these actions. All users with access to the patient form can see SVL statuses. Important Notes 🔸 Locking a variable or category prevents changes via API and ePRO 🔸 Deleting and restoring a patient keeps SVL statuses intact 🔸 SVL for patients, categories, and variables are independent (e.g., unlocking a patient won’t unlock a category or variable) Who can use this feature? Available to all paid plans and free trials Can be used in any study where SVL per category/variable is enabled 🚀 This feature makes data monitoring more efficient and structured, ensuring better compliance and reliability in clinical research!

In clinical trials, each patient inclusion or adverse event declaration represents a key moment that requires heightened attention. At EasyMedStat, we are committed to helping you optimize your processes by introducing a new feature: Monitoring Automations. Why is this feature important? Managing multiple clinical studies simultaneously can be challenging. In such a context, it’s easy to miss critical information, such as the inclusion of a new patient or the declaration of an adverse event. With our new feature, you can automate email notifications as soon as a patient is included or an adverse event is declared. This allows you to react quickly while avoiding human errors. How does it work? Monitoring Automation is based on a simple principle: you define an action that is automatically triggered by a specific event, such as patient inclusion or an adverse event declaration. Let’s look at two use cases: Inclusion of a new patient: When the inclusion of a new patient is validated in your eCRF, an email is automatically sent to the clinical research team. You can customize this message with variables related to the patient, the user, or the inclusion site, allowing the email to be contextualized according to your specific needs. Adverse event declaration: When an adverse event is declared, an email can be sent to the regulatory affairs team. It is also possible to set a condition based on the severity of the event. For example, only serious adverse events can trigger a notification. A valuable time-saver for your teams Monitoring Automations offer incredible flexibility. Instead of constantly checking inclusions and events across your various studies manually, you can now rely on these automatic notifications to keep you informed in real time. This feature not only improves the responsiveness of your teams but also helps avoid oversight or delays in processing critical data. Customization and flexibility One of the main advantages of this feature lies in its customization. Whether it’s the email subject, content, or recipients, everything can be tailored to your needs. You can insert variables related to patients (such as inclusion date, patient ID) or users (first name, last name), ensuring that each notification contains relevant information. Additionally, it is possible to configure notifications specific to one or more sites , depending on the setup of your study. For example, you can choose to receive notifications only for inclusions made at certain centers. Conclusion With this new feature, EasyMedStat takes another step forward in supporting clinical research teams. By automating essential tasks such as notifications for patient inclusion or adverse events, you enhance both the efficiency and safety of your trials. Don’t wait to explore and test Monitoring Automations in your EasyMedStat interface! Stay connected, stay responsive, and focus on what matters most: the success of your clinical trials.

New Features in EasyMedStat: Custom Record ID (CRID) and Test/Production Modes [Product Update 3.36]
We are pleased to announce two important updates in EasyMedStat that enhance the flexibility and reliability of your clinical research workflows: Custom Record ID (CRID) and Test/Production Modes. These features provide you with better control over patient identifiers and the ability to switch between testing and production environments with ease. Here’s an overview of what’s new and how it can benefit your research. Custom Record ID (CRID) for Improved Patient Management In clinical research, tracking participants through clear and consistent identifiers is critical. To support this, EasyMedStat now offers the option to customize patient identifiers through the new CRID feature. You can define a custom pattern for generating unique patient IDs, which can include both numeric and alphanumeric elements. This system ensures that patient identifiers are automatically generated, non-editable, and incremented sequentially, minimizing errors and maintaining consistency. Key features of CRID: Customizable Formats : Define the structure of your identifiers (e.g., 001, AA-001, or MC-PAR-001 for multicenter studies). Multicenter Support : Generate site-specific identifiers using predefined patterns like the site’s initials or a numeric code. Global or Site-Specific Counters : Choose between a single counter for the entire study or independent counters for each study site. This feature helps streamline patient identification, making it easier to manage participants across different sites and reducing the risk of data mismanagement. You can learn more in our knowledge base: How to Customize the Patient Identifier? (AA-001, ...) Test/Production Modes for a Safe Transition to Live Data In addition to CRID, we’ve introduced the Test/Production Mode to make transitioning your study from development to active data collection more straightforward. During the early stages of a study, you often need to test settings, workflows, and data entry processes without risking real patient data. Now, you can start in Test Mode, where everything can be experimented with, and then move to Production Mode when you’re ready to collect live data. Key benefits of Test/Production Modes: Safe Testing Environment: While in Test Mode, you can freely configure series settings, including CRID patterns, without affecting the actual study data. Controlled Transition to Production: When your study is ready, you can switch to Production Mode, locking in key configurations such as the CRID settings, and ensuring no accidental resets of incremental counters. Secure Data Management: Once in Production Mode, patient data and records are locked to ensure that no unintended changes disrupt the study. These modes allow for flexibility and peace of mind, helping you prepare and validate study settings before launching them in a live research environment. Conclusion With the introduction of Custom Record ID (CRID) and Test/Production Modes, EasyMedStat continues to provide tools that enhance your study management and data integrity. The new features support a more organized and secure clinical research process, whether you're managing a single-site study or a complex multicenter project. These updates are available now for all users . We encourage you to explore these features in your next study setup to see how they can streamline your research workflows and data management.
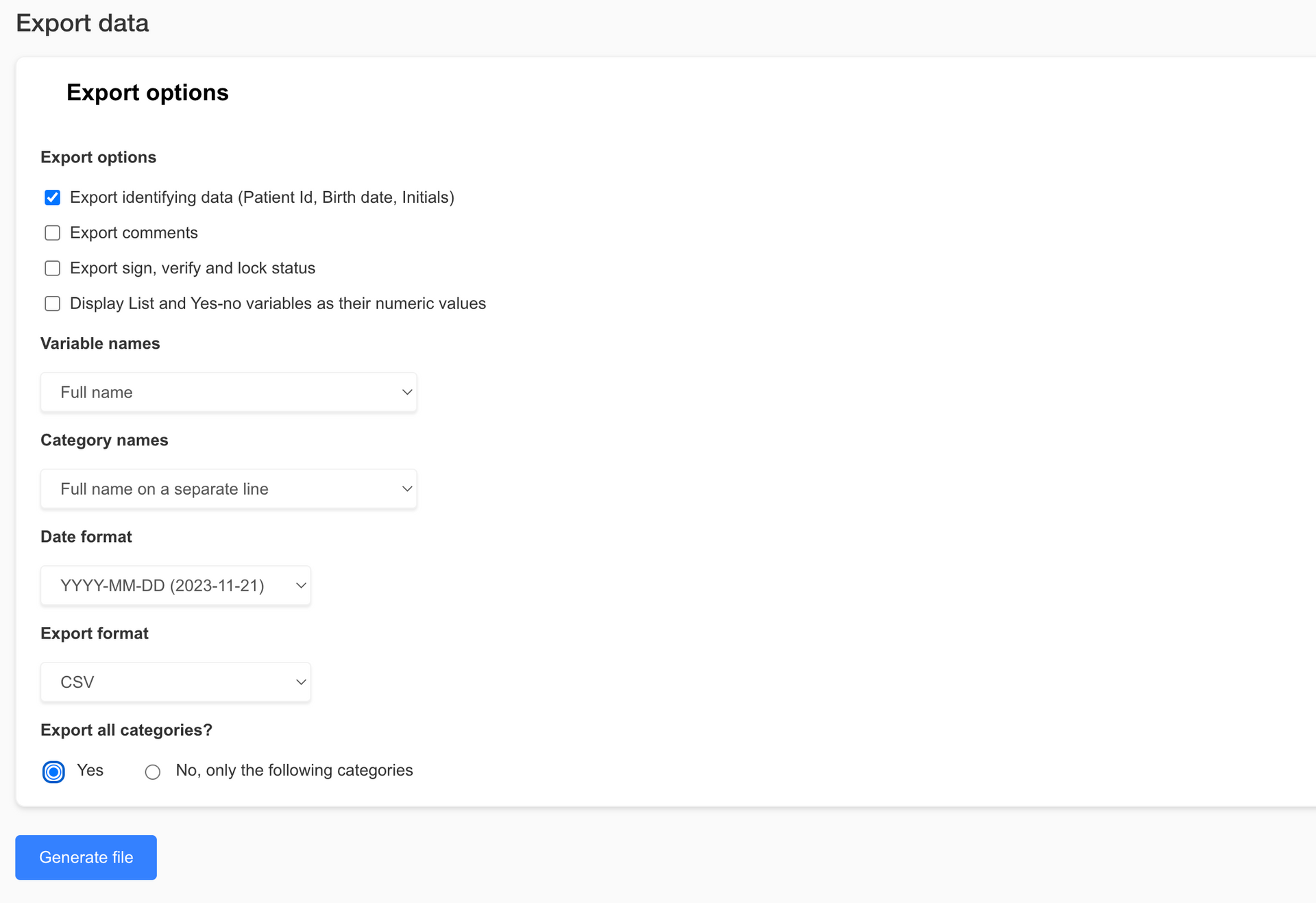
We are excited to announce the latest version of EasyMedStat, packed with new features and improvements designed to make your clinical research processes smoother and more efficient. This update brings big enhancements to our data export capabilities, collaboration tools, category management, and eCRF viewing options. Let's dive into what's new and how these features can benefit you and your team. Revamped Export Data Page Exporting data is now easier and more versatile than ever. Check out the new features on our revamped Export Data page: - Enhanced Export Options : Whether you need the entire dataset or just a specific part, our new options allow you to export exactly what you need. This helps keep file sizes manageable and your data focused. - Excel Format Export : You asked, and we listened! You can now export your data in Excel format (.xlsx), making it super easy to work with in your favorite spreadsheet software. - Pseudonymization : Protect patient privacy by exporting pseudonymized data. It's a great way to ensure data security while still getting the insights you need. - R-Compatible Exports : If you use statistical software like R, you'll love our new export options. Now you can export coded values and variable names without spaces or special characters, making data import into R a breeze. Share with Collaborators Page Update Collaborating with your team just got simpler with our updated Share with Collaborators page: Select All Option : Need to assign permissions to a collaborator quickly? The new "Select All" option lets you do just that, saving you time and hassle. Revamped Category Picker Managing categories is now more intuitive thanks to our revamped Category Picker: - Hierarchical Display : Easily navigate through categories with a clear, expandable tree structure. - Select All and Search Functionality : Quickly select all categories or find specific ones using the search bar. Real-time filtering and a selection count display make managing categories a snap. Enhanced Viewing Capabilities for Users with "View Patient" Permission We’ve boosted the viewing capabilities for users with "View patient" permission to enhance monitoring and data access: - View and Download Files and Pictures : Users with "View patient" permission can now see and download pictures and files directly from eCRF v2. - Streamlined Interface for Non-Editors : For users without "Edit patient" permission, we’ve streamlined the interface by removing editing options while keeping full viewing functionality. Conclusion These nifty new features and improvements are designed to make EasyMedStat more powerful and user-friendly. We’re confident these updates will help you collect, analyze, and share your data more efficiently and securely. We can’t wait to see how you use these tools to advance your research and improve patient outcomes. Stay tuned for more updates, and as always, we love hearing your feedback. Thanks for choosing EasyMedStat as your go-to platform for clinical research!
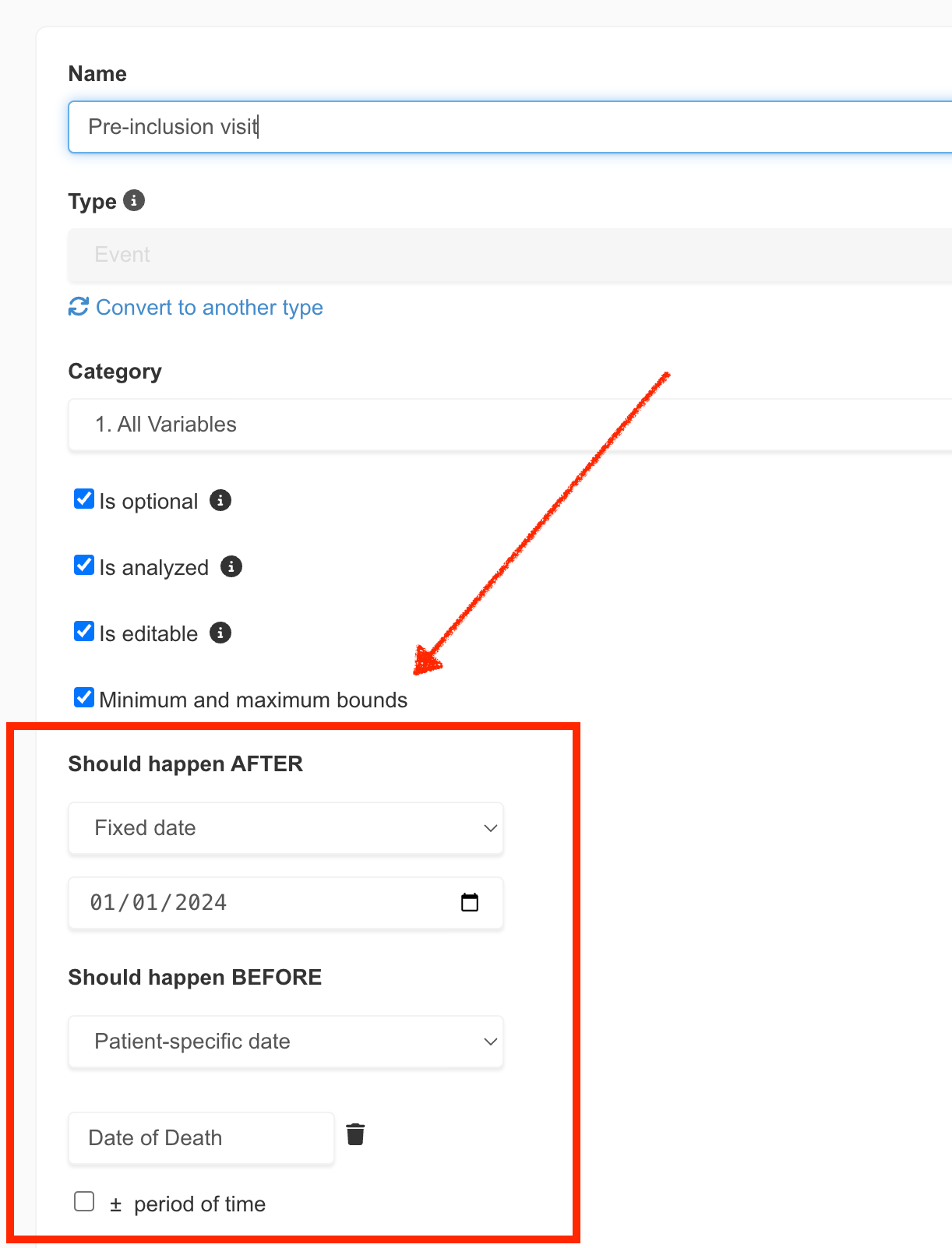
In the realm of clinical research, precision is not just a goal; it's a necessity. Recognizing this, EasyMedStat is excited to unveil a groundbreaking feature that marks a significant leap forward in data management and quality control: Event Bounds. This new addition is designed to streamline the data entry process, enhance accuracy, and reduce the time spent on data monitoring. Let's dive into what Event Bounds entail and how they promise to transform clinical data management. What are Event Bounds? Event Bounds are a novel feature that allows users to set minimum and maximum date limits for Event variables within Electronic Case Report Forms (eCRFs). This functionality extends beyond the static boundaries applied to Numeric variables, offering both static (fixed dates) and dynamic (patient-specific dates) bounds. Dynamic bounds are particularly innovative, as they adjust based on the values of other Event variables, providing a tailored and flexible approach to data entry.

We are thrilled to announce the release of our latest feature: Propensity Score Matching (PSM). This groundbreaking tool revolutionizes the field of clinical research by empowering researchers to enhance the quality and comparability of their studies. In this blog post, we will delve into the significance of PSM, its relevance in clinical research, and how to access this game-changing feature on EasyMedStat. The First Propensity Score Matching Guided Tool for Clinical Research We are proud to be the pioneers in introducing a guided tool for propensity score matching in the realm of clinical research. Our team of experts has developed a robust algorithm that facilitates the identification and pairing of subjects based on key characteristics, ensuring a more balanced and rigorous comparative analysis. With our PSM Guided Tool, researchers can now conduct propensity score matching analyses with confidence , knowing that the tool automates the critical checks for the required assumptions . These include ensuring the appropriate number of covariates, assessing group comparability, validating the common support assumption, and more. By streamlining and automating these crucial steps, we empower researchers to focus on their analysis and interpretation, knowing that the tool has their back. What is PSM? And Why Does It Matter? Propensity Score Matching (PSM) is a statistical technique used to control for potential confounding variables in non-randomized studies . It aims to create comparable groups by balancing the distribution of covariates between treatment and control groups. By doing so, PSM helps minimize the impact of confounding factors, thereby improving the internal validity of the study and strengthening the evidence obtained. PSM matters because it allows researchers to address the inherent limitations of non-randomized studies . It enables researchers to account for differences in patient characteristics and minimize bias, leading to more reliable and meaningful results. How to Perform a Propensity Score Matching? To access the propensity score matching feature on EasyMedStat, follow these simple steps: Navigate to the menu "Statistics" and Click on "Compare groups" to initiate the comparative analysis. Choose the groups you want to compare Click on "Match groups to improve comparability." Select the covariates you want to base the matching on, ensuring they are relevant to your research question. Verify the methodology with our built-in methodology tool, which provides transparency and ensures the accuracy of the matching process. With EasyMedStat's user-friendly interface and step-by-step guidance, researchers can seamlessly incorporate propensity score matching into their study design, ultimately enhancing the reliability and validity of their findings. Propensity Score Matching (PSM) is a powerful tool that significantly contributes to the advancement of clinical research. EasyMedStat's guided PSM feature empowers researchers to tackle the challenges of non-randomized studies and improve the quality of their research. By leveraging the benefits of PSM, researchers can obtain more robust and reliable results, leading to better-informed medical decisions and improved patient care. Unlock the potential of Propensity Score Matching with EasyMedStat and take your clinical research to new heights!

During a clinical investigation on a medical device, it is crucial to select the appropriate clinical scores to accurately assess its effectiveness. Clinical scores provide quantifiable and standardized measurements, enabling an objective evaluation of clinical outcomes. In this article, we explore the different steps to choose the suitable clinical scores for your clinical investigation on medical devices. Analyze the Scientific Literature A fundamental step in selecting the appropriate clinical scores is to conduct an in-depth analysis of the existing scientific literature. This analysis helps discover validated clinical scores used in previous studies on similar medical devices. By relying on the accumulated knowledge and expertise in the field, one can ensure the relevance of the selected clinical scores. Consult Your Investigators! Working closely with investigators ensures that the chosen clinical scores align with the needs of the clinical investigation. Their expertise and practical experience are invaluable in selecting the most appropriate clinical scores based on the medical device and study context. Another advantage of co-constructing the observation form with investigators is that they are often familiar with certain clinical scores used in their daily medical practice. Hence, they can more easily collect the same scores for your clinical investigations. Limit the Number of Scores to the Minimum It is essential to limit the number of clinical scores in the observation form. By avoiding information overload, data collection and statistical analysis are simplified. Typically, one to two relevant clinical scores are sufficient to evaluate the effectiveness of a medical device. By focusing on the most significant and directly related measures to the study's objective, clearer and more actionable data are obtained. Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) Patient-reported outcome measures, or PROMs, are valuable tools for gathering data directly from patients. They provide information about their health status, symptoms, and quality of life. However, it is important to consider the potential fatigue associated with repeated completion of these questionnaires , especially if using redundant questionnaires or sending them at a high frequency. To minimize fatigue, it is necessary to use concise and targeted patient questionnaires, avoiding redundant or irrelevant information. A well-designed questionnaire encourages patient participation and ensures more comprehensive data. Choose the Questionnaire Requiring Fewer Responses in Case of Equivalence When faced with two highly correlated questionnaires, it is advisable to choose the one that requires fewer responses from patients or investigators. This simplifies data collection, encourages patient and investigator participation, and reduces monitoring efforts. By ensuring simplicity and user-friendliness in questionnaires, more complete and higher-quality data are obtained. The Importance of Subscales in Clinical Scores Some clinical scores include specific subscales that evaluate particular aspects of a medical device's effectiveness. For example, a functional score may provide subscores evaluating pain, mobility, or daily activities. A quality of life questionnaire may provide subscores on the mental health of patients. These subscales provide detailed and in-depth information on specific domains. Including these relevant subscales allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of the impact of the medical device. Conclusion Choosing the right clinical scores is crucial for a successful clinical investigation. By following the outlined steps, including analyzing scientific literature, consulting investigators, limiting the number of scores, and considering patient questionnaires and subscales, high-quality data can be obtained to assess the performance of your medical device. Close collaboration with investigators and attention to patient questionnaires and subscales contribute to a precise and comprehensive evaluation of the effectiveness of medical devices.